|
|
| This software is designed by Didier Grzejszczak and improved a first time in 2012 by Hervé Locteau, and a second time by Ahmad Montaser Awal between september 2013 and August 2014 |
|
|
|
The principle: The system is composed of several sub-steps:
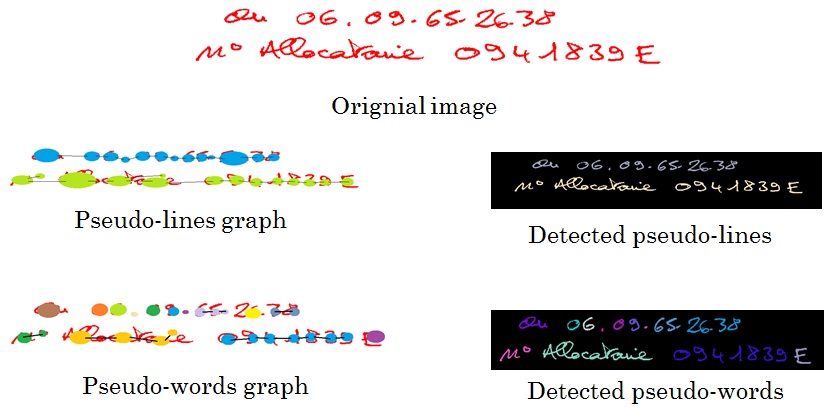
This is done by a double smearing, a first 'Smearing' to extract document lines. Then, an analysis of the gaps between the CCs can find pseudo-words. 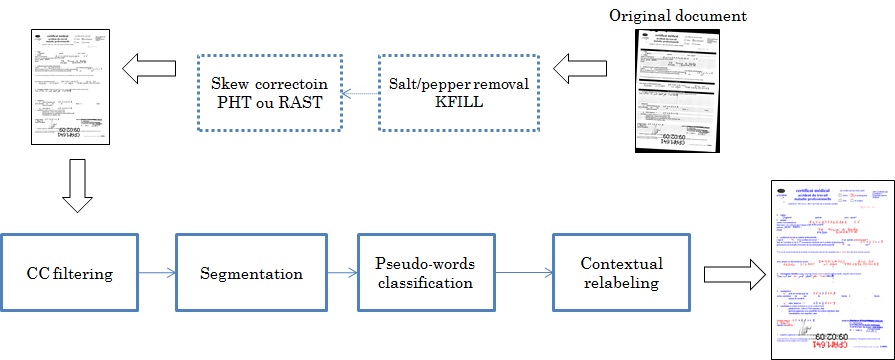
Segmentation and classification Differently from most of existing works, the document is first segmented into pseudo-lines before being segmented into pseudo-words. Pseudo-line are set of connected
components where horizontal distances and vertical distances are less than
thresholds. Pseudo-words are considered as set of connected components belonging to the same pseudo-line. The extraction is made possible using an adjacency and linear graph.
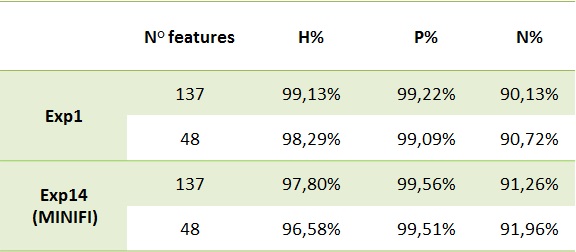
Each pseudo-word is described by several descriptors providing 137 features. An SVM multi-class is used to classify a pseudo-word into: Handwritten text, Printed text or Noise.
Contextual re-labelling Contextual information is exploited by considering the neighbourhood to relabel the pseudo-words. Different techniques have been used.  Results The training was done on a DB of 75 documents (10173 pseudo-words shared as H: 2357; P: 4892; N: 2924). The testing DB contains 24 documents (~7669pseudo-words shared as H:1191; P: 4218; N: 1934). All documents are label at the pixel level 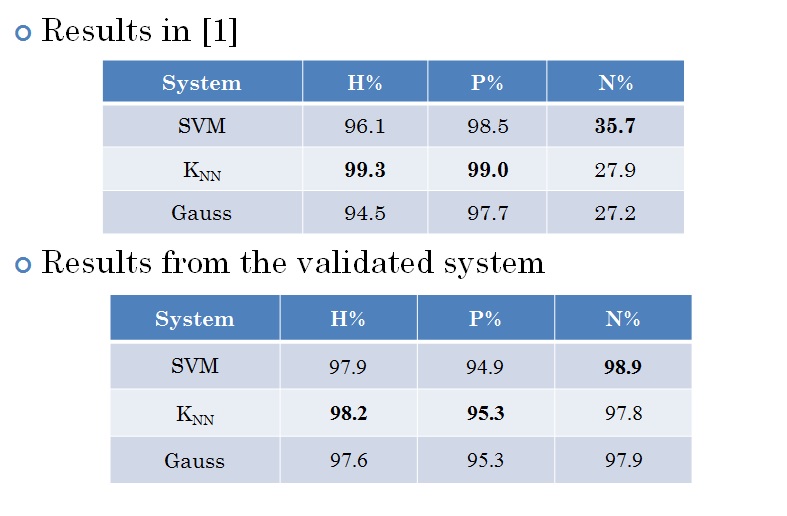 |
|
|
|
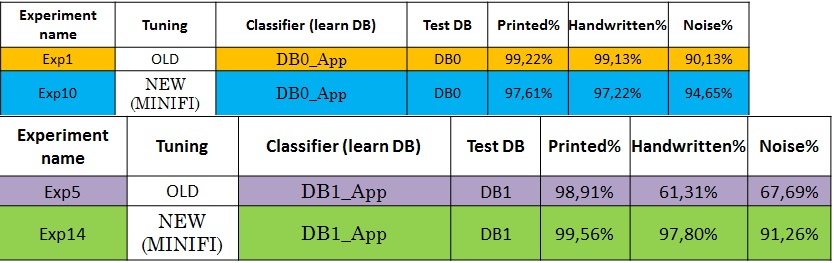
Several improvements have been provided by Ahmad Montaser Awal. They are described below: New datasets Training DB_T0 (new): 107 documents (32706 pseudo-words), H: 5888; P: 18078; N: 8740. Test DB0 (new): 202 documents (~82142 pseudo-words): H: 11970; P: 43705; N: 25190. All documents are label at the pixel level Horizontal overlapping 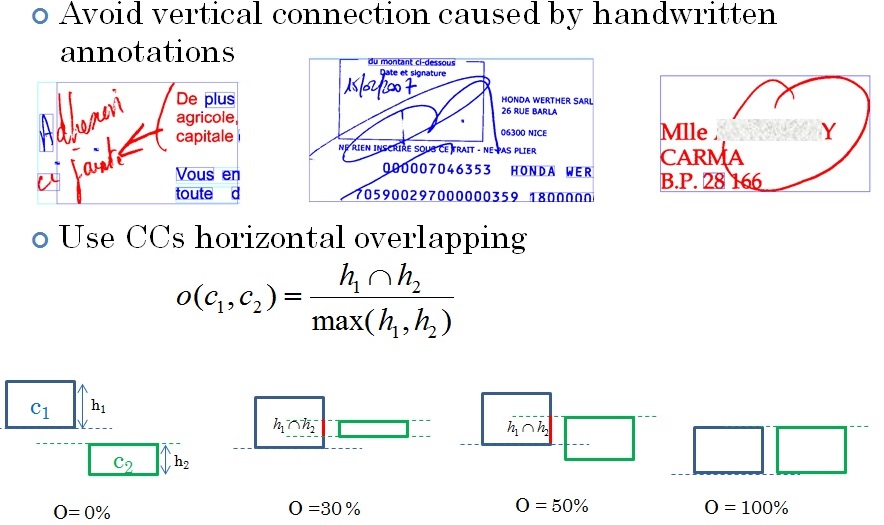 Line detachment  MLP and classifier combination A combination between MLP and SVM is performed. 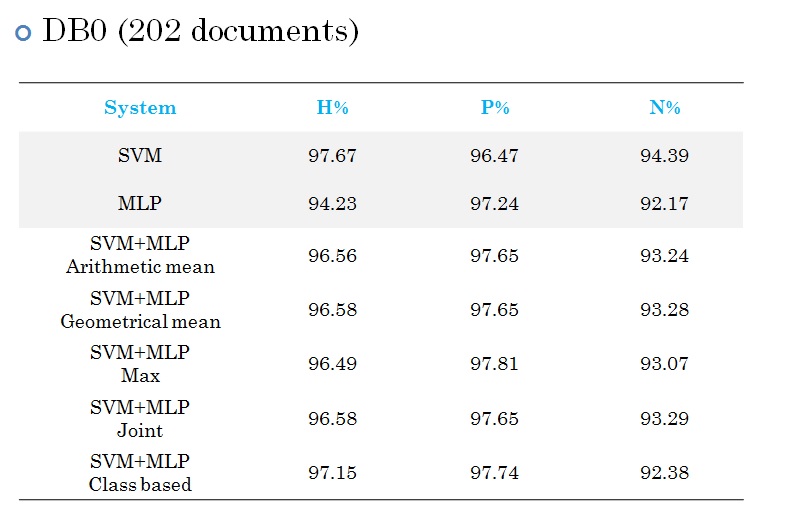 Contextual re-labelling by CRF 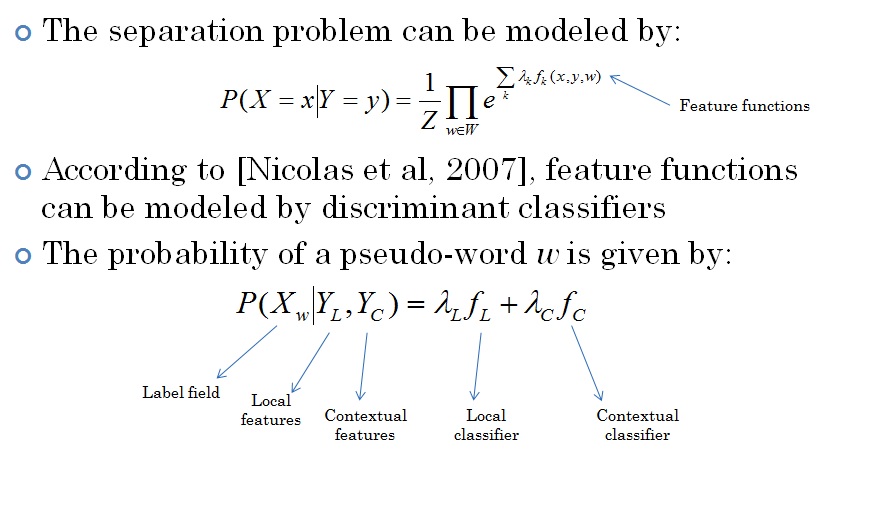 Re-labelling using pseudo-lines  Re-labelling using dominant class of line 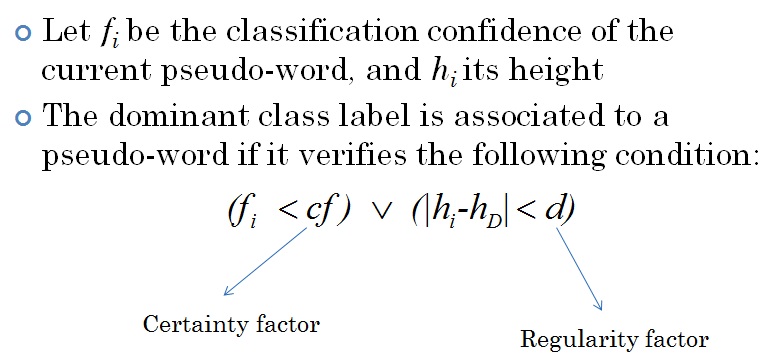 Example  Results 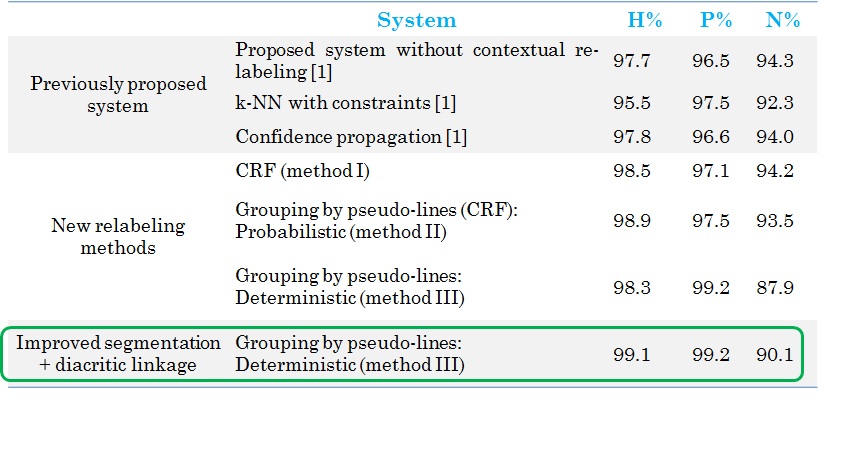 System specialisation Three adaptations have been made for:
 Feature selection
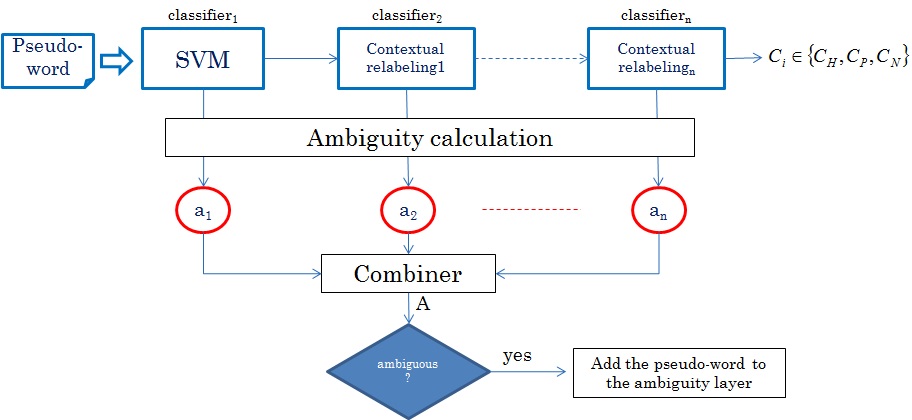
 Ambiguity layer
 Pseudo-word Ambiguity 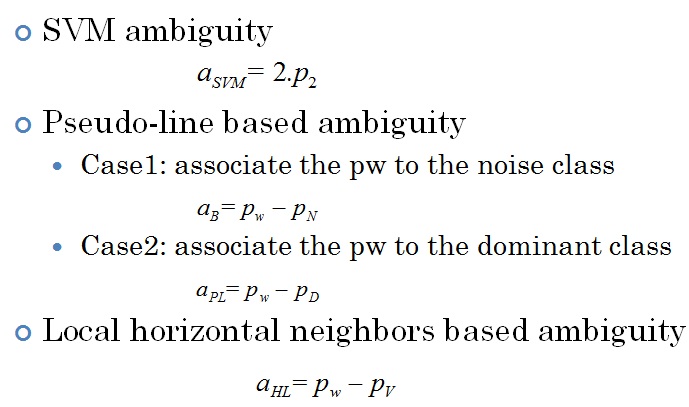 Ambiguity fusion  Ambiguity layer evaluation 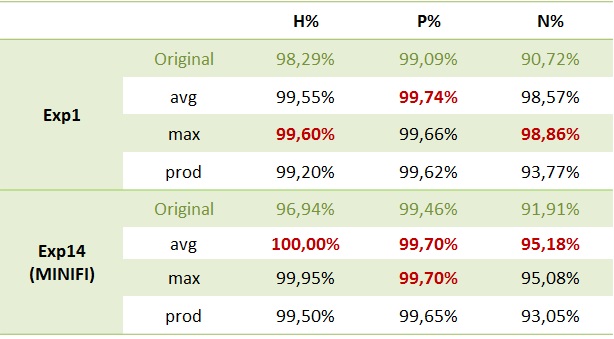 |