|
|
|
|
|
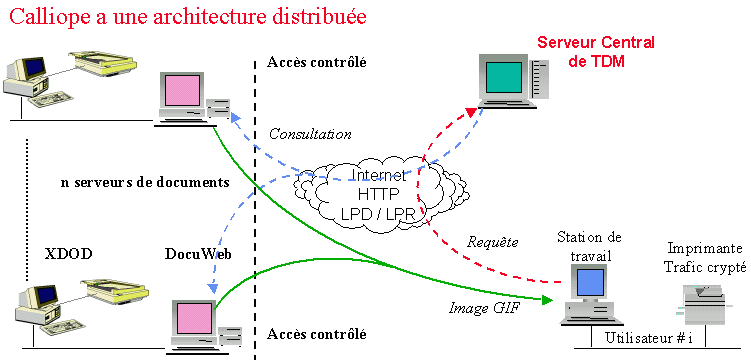
TDM est un logiciel associé à Calliope pour reconnaître des tables de matières, les structurer et les ajouter au serveur From a request for an article made by the user, the system launches a request to the central waiter to check the presence of the article. In the event of success, the article is required on the document servers. If the article is not digitized, then a request for digitalization is made to the documentalist. If the article is already digitized, then it is returned to the user in form image. The exchange is done through the Web by simple protocols HTTP. TDM is a software associated with Calliope to recognize matter tables,
to structure them and add them to the server.
|
|
|
|
|
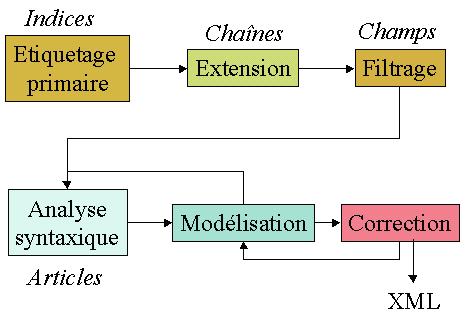
The technique used is based on labelling by part of speech. After a primary labelling of the words by their morphological category, a first grouping is operated. Then, these words are gathered in chains forming the searched fields. The words not recognized by OCR and thus badly labelled are included in the surrounding chains if the context allows it, from where interest of this type of labelling. For the erroneous articles, a syntactic anlyzis is carried out on the
correct articles, then the model extracted from this analysis is used to
correct them.
|
|
|
|
| Primary labelling
Le texte est examiné ligne par ligne, puis
chaque ligne, espace et mot dans la ligne est étiqueté suivant
les étiquettes morphologiques associées. Une tabulation
TB est un espace long et régulier, CN représente un nom commun,
PN représente un nom propre, IT représente un prénom,
The text is examined line by line, then each line,
spaces and word in the line is labelled according to the associated morphological
labels. A tabulation TB is a long and regular space , CN represents a common
noun, PN represents a proper name, IT represents a first name, UN represents
an unknown word, because it either absent in the dictionaries, or is badly
recognized by the OCR.
|
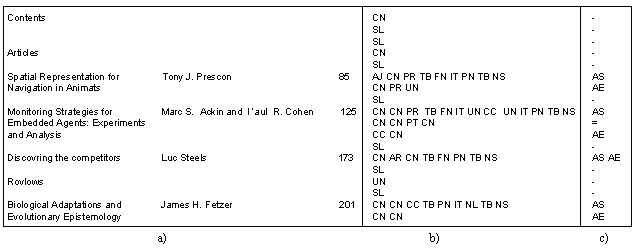 |
| Secondary labelling
Les étiquetages sont regroupés et des champs sont identifiés. Tit représente le titre, Aut représente l'auteur et NS représente le numéro de page. La colonne (a) montre un exemple de formulaire. La colonne (b) montre encore desxmots inconnus qui ont été regroupés dans la colonne (c) Labellings are gathered and fields are identified. Tit represents the title, Aut represents the author and NS represents the page number. The column (A) shows an example of Table of contents. The column (b) still shows some unknown words which were gathered in the column (c)
|

|
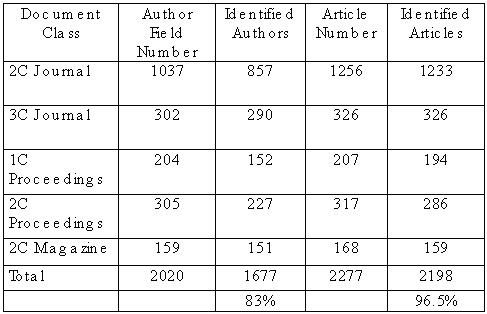
| Resultts
Nous avons testé ce prototype sur 32 revues et 9 congrès, comptant 2277 articles et 2020 champs auteurs. Le taux de localisation des articles est de 96,5%. Les articles ont été localisés complètement dans 81% des sommaires. Un seul sommaire a moins de la moitié des articles localisés, ce sommaire comporte des erreurs de structuration. Le taux de reconnaissance des champs est de 96,5% pour les numéros de page et de 83,0 % pour la séparation des titres et des auteurs. Les auteurs ont été identifiés complètement dans 40% des cas, et 4,5% des cas ont été identifiés à moins de 50%. We tested this prototype on 32 reviews and 9 congresses,
containing 2277 articles and 2020 fields authors. The rate of localization
of the articles is 96,5%. The articles were localized in 81%
of the synopses. Only one synopsis has less than half of the located
articles, this synopsis comprises errors of structuring. The recognition
rate of the fields is 96,5% for the numbers of page and 83,0 % for the
separation of the titles and the authors. The authors were
|
 |
|
|
|
The image on the right-hand side is the result in XML of the recognition of the table of content on the left. One represented in fat the title, the numbers of page are accompanied by the letter p. the system is connected to an image server of articles which deliver them while clicking on "Request for photocopy". |
 |